Understand the importance of brain health
Brain health is an important aspect of overall well-being, and a growing body of research emphasizes the brain's importance in determining cognitive performance as we age. Factors that contribute to maintaining brain health and protecting against cognitive decline are multifaceted and include factors such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and a healthy gut microbiome. Of particular interest is a gut bacterium known as A celatus that has been previously associated with executive function.
The impact of a healthy lifestyle on cognitive function
A cohort study reported in JAMA Network found that higher lifestyle scores, which indicate a healthier lifestyle, were associated with better cognitive function in older adults. Data from the Rush Memory and Aging Project used in the study showed that factors such as physical activity, diet, and cognitive activity contributed to this score. The study concluded that a healthy lifestyle may provide cognitive reserve that preserves cognitive performance, independent of the common neuropathology of dementia.
Healthy lifestyle choices and cognitive decline
Another study published in JAMA Neurology echoed these findings, finding that healthy lifestyle choices can slow cognitive decline, even in older adults with neuropathology such as dementia. suggests that it is possible. These healthy lifestyle choices include being physically active, eating a healthy diet, avoiding smoking, and limiting alcohol intake. There is consistent evidence that a healthy lifestyle has many benefits for cognitive function and may reduce the risk of dementia.
Physical activity, cognitive stimulation, and brain health
Physical activity and cognitive stimulation are essential components of a healthy lifestyle that boosts brain health. These activities help increase blood flow to the brain, improve heart health, increase brain activity, and increase brain volume. It may also prevent neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in the brain. Experts recommend 150 minutes of physical activity a week, spending time with friends and family, and doing cognitively stimulating tasks to protect cognitive function.
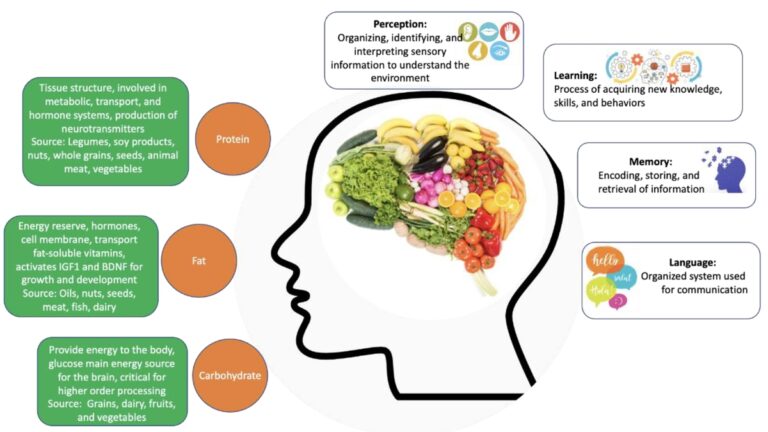
The role of diet in maintaining optimal brain health
Eating a balanced diet is another cornerstone of a healthy lifestyle that can protect cognitive function. The composition of the gut microbiota is influenced by diet and may play an important role in maintaining optimal brain health. For example, a specific gut bacteria, A celatus, can have a positive impact on executive function.
Frailty, pain, and cognitive function
A cross-sectional study conducted in South Korea investigated the effects of frailty severity and severe pain on cognitive function in community-dwelling older adults with arthritis. Interestingly, this study found that severe pain alone did not significantly impact cognitive function. Therefore, it is essential to assess both pain and frailty severity to predict high-risk groups and provide appropriate interventions to prevent cognitive decline.
Lifestyle factors and dementia pathology
Scientists at Rush University Medical Center investigated whether brain pathology associated with dementia alters the association between healthy lifestyle choices and cognition later in life. Their findings showed that a healthy lifestyle was associated with near-death cognitive decline, regardless of Alzheimer's disease or dementia-related brain pathology. Independent of the effects of vascular disease, lifestyle factors such as physical activity and diet are also associated with lower cognitive decline.
Boosting resilience against dementia through a healthy lifestyle
With more than 55 million people worldwide affected by dementia and 10 million new cases occurring each year, the study published in JAMA Neurology suggests that more steps can be taken to reduce the risk of developing dementia. This highlights the urgent need for research. The study found that people who lead healthy lifestyles may be more resistant to changes in the brain that can cause symptoms of dementia. Therefore, higher lifestyle scores based on the five lifestyle factors were associated with better overall cognitive function as an older adult.