This study was conducted as an extension of the Erfurt Neurofibromatosis Database Study (NF Registry). This database contains disease data for patients diagnosed with neurofibromatosis. NF2-SWN. This database is an online registry on the Castor EDC platform that complies with European data protection laws. This registry has been approved by the local institutional review board and collects pseudonymized patient data. Updated regularly after each inpatient or outpatient visit. This study was approved by the local ethics committee in Erfurt (ref:2278/2020/6). All patients provided written informed consent.STROBE guidelines for cross-sectional studies were used13. This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
The public web-based survey was conducted from December 2021 to January 2022 using the SoSci Survey online tool. N= 97 patients at the Erfurt Neurofibromatosis Center were invited via email to voluntarily participate in an online survey. The survey included questions about age, gender, and date of birth. Date of birth in the survey data had to match the data in the NF registry. Inclusion criteria were a diagnosis of “.NF2“Associated schwannomatosis” and minimum age of 16 years.
severity of illness
The clinician-reported disease severity score consists of seven symptoms that significantly impact a patient's life. (1) Hearing loss in both ears. (2) Severe visual impairment in both eyes. (3) Bilateral facial paralysis, at least on one side with her H&B°3 or higher. (4) Depression/anxiety disorders. (5) Severe chronic pain/substance abuse due to pain. 6) Immobility. (7) Malignant tumor9. If all points are not present, severity is rated as mild, with 1 to 3 symptoms indicating moderate severity, and 4 to 7 symptoms being reported as severe. NF2-SWN. Disease severity scores range from 1 (=mild) to 3 (=severe). Participants' disease severity was assessed based on NF registry data. Disease severity scores were derived from the most recent clinical data available in the NF registry. This score has been validated (currently under consideration for publication), and a version of it has been described in detail in a recent publication.9.
Health-related quality of life
Hornigold et al. (2012) developed the Neurofibromatosis 2 Impact on Quality of Life (NFTI-QoL) questionnaire to assess his health-related QoL. NF2– SWN patients. This 8-item questionnaire assesses a variety of disease-specific areas, including balance, hearing, facial weakness, vision, mobility/gait, life role/outlook, pain, and anxiety/depression. Each item consists of his 4-point rating from 0 to 3, with 3 being the most impaired. The maximum total score is 24. The higher the NFTI-QoL score, the worse the outcome. The German version (NFTI-QoL-D) demonstrated comparable metric properties to the English-speaking version.9.
mental health problems
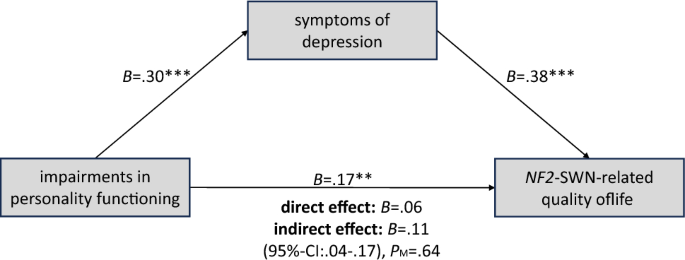
symptoms of depression
The Nine-Item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) is a self-administered survey developed for depression.14. Each item on the PHQ-9 is quantified on a 4-point Likert scale (0 = “not at all”, 3 = “almost every day”). The total score ranges from 0 to 27, with 0 indicating no symptoms of depression and 27 indicating all symptoms occur nearly every day.
The PHQ-9 has excellent test/retest reliability and good criterion and construct validity.14. Internal consistency has been verified (Cronbach's α = 0.89). Furthermore, different types of depression, including mild (0–4), mild (5–9), moderate (10–14), moderately severe (15–19), and severe (≥20) depression. Threshold scores exist to identify severity levels. A score of 10 or higher has been shown to have a sensitivity of 88% and a specificity of 88% for major depression in the general medical population.14.
anxiety symptoms
The Generalized Anxiety Disorder Questionnaire (GAD-7) is a 7-item self-report scale developed to assess symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder.15. Items are rated on a 4-point Likert scale (0 = “not at all”, 3 = “almost every day”). The GAD-7 items describe some of the most important diagnostic criteria for generalized anxiety disorder (tension, anxiety, irritability, worrying too much, etc.). The total score ranges from 0 to 21, with higher scores indicating more severe symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder. Research suggests that the GAD-7 is a valid screening tool for generalized anxiety disorder and a tool for assessing its severity in clinical practice and research.15,16. GAD-7 also defines threshold scores for different severity levels. Mild (0–4), mild (5–9), moderate (10–14), and severe (15–21) anxiety symptoms. A GAD-7 total score of 10 or higher represents a moderate to severe level of generalized anxiety and indicates a probable diagnosis of generalized anxiety disorder. The GAD-7 showed good sensitivity (89%) and specificity (82%) for detecting generalized anxiety disorder in primary care patients, and its internal consistency was also excellent (Cronbach's α = 0.92).
physical symptoms
Somatic symptom burden was measured using a self-report questionnaire, the Somatic Symptom Scale (SSS-8). The SSS-8 was developed as an 8-item shortened version of the PHQ-15 to assess the presence and severity of common physical symptoms.17. The SSS-8 assesses the severity of the following physical symptoms experienced by respondents in the past 7 days: (1) Stomach or intestinal problems. (2) Lower back pain. (3) Pain in arms, legs, and joints. (4) Headache. (5) Chest pain or shortness of breath. 6) Dizziness. (7) Feeling tired or low in energy. (8) You have a sleep disorder. Each item is quantified on a 5-point Likert scale (0 = “not at all”, 4 = “extremely”). The total score ranges from 0 to 32, with higher scores indicating more physical symptoms. The severity threshold score defines five different levels of physical symptom burden: none, minimal (0–3), low (4–7), moderate (8–11), and high (12–15). and very high (16–32) physical symptoms. Cases with high physical symptom burden were between the 95th and 98th percentiles. The German version of SSS-8 has been validated in the German general population18.
psychological factors
Resilience
The 13-item Resilience Scale (RS-13) quantifies resilience on a 7-point scale.19. Individuals rate different statements (from 1 = “disagree” to 7 = “completely agree”). The RS-13 is a shortened version of the German version of his RS-25.20. Scores range from 13 to 91, with higher scores indicating greater resilience. Based on the reference group, individuals with less than 72 points on the Resilience Scale (RS-13) are defined as individuals with low resilience.Highly resilient people score 72 or higher19.
loneliness
Loneliness scaletwenty one It consists of three items: “How often do you feel…?” (1) “…do you feel like you have no friends?”; (2) “…left behind?” (3) “…isolated from others?” Items are on a 5-point Likert scale (0 = “Not at all”). Ratings range from “never'' to 4 = “very often.'' Responses are summed to yield a total score ranging from 0 to 12, with higher scores indicating higher levels of loneliness.The German version of the 3-item loneliness scale was validated in a representative sample and standard values are reported.twenty two.
personality functions
Personality functioning describes a person's abilities in four areas related to cognition/perception, regulation, communication, and attachment.twenty three. People with impaired personality functioning tend to suffer from severe impairments in self and interpersonal relationships and are at increased risk of developing mental illnesses such as depression and anxiety.twenty four. Personality functioning was measured using a shortened version of the Operationalized Psychodynamic Diagnostic Structure Questionnaire (OPD-SQS).twenty five. A self-report questionnaire to screen for personality disorders.26. The OPD-SQS consists of a 0–4 Likert scale (0 = “totally disagree” to 4 = “totally agree”). It measures three highly correlated subscales: self-awareness, interpersonal contact, and relational model. The total score ranges from 0 to 48. Lower OPD-SQS scores indicate better personality functioning, whereas higher OPD-SQS scores indicate impaired personality functioning.
statistical analysis
Data analysis was performed using IBM SPSS (version 20). Since a single value was missing from the questionnaire, the mean replacement method was applied. Isolated single missing values within a questionnaire were replaced using the rounded individual mean of each questionnaire. This was performed once for each case of PHQ-9, SSS-8, and OPD-SQS. Patients with more missing items in the same questionnaire were excluded from the questionnaire analysis. This was performed once for each case of GAD-7 and SSS-8. Missing values on the NFTI-QoL-D were replaced with rounded item means. Descriptive statistics included age, gender, NF2-SWN-related QoL, depression, anxiety, physical symptoms, resilience, loneliness, and personality functioning.
First, we calculated Pearson correlations between different variables to examine their associations. Next, a stepwise hierarchical linear regression analysis was performed. This includes: NF2– SWN-related QoL as dependent variable. Three groups of variables served as predictor variables and were entered into the equation stepwise. The first predictors were disease severity score and gender. In step 2, values for resilience, loneliness, and personality functioning were entered stepwise as potential psychological predictors. The third group of variables includes scores for depression, anxiety, and physical symptoms as indicators of mental health problems, which are also entered in stages. Adjusted R squared (R2) and standardized regression coefficients (β) were reported.The results were considered significant p< 0.05.