Economies are increasingly decoupling economic growth from carbon emissions to address the challenges faced by climate change. Recognizing the consequences of delayed action, low-carbon transition stages are already underway in many developing countries. This requires a systematic approach to transformative, system-wide change, especially in the energy sector, which is the world's largest carbon emitter. This also requires significant changes across multiple dimensions, including technology, capacity building, and various enablers.
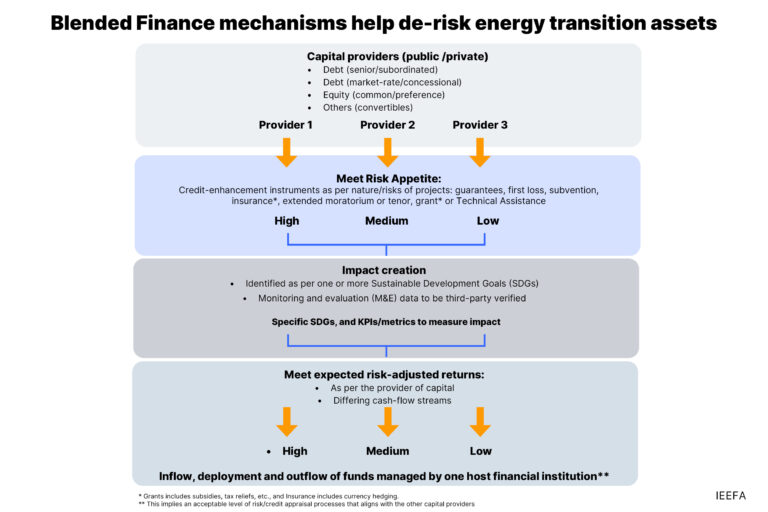
Such a transition path in the energy sector requires significant financial flows. While technology, capacity and other enablers are essential, there is a need to clearly articulate an acceptable risk-adjusted return model beyond utility-scale renewables, especially to secure funding from commercial sources. For-profit organizations focus on risk and return, assessing risk based on factors such as proven business models, cash flow visibility, and borrower credentials, but these are interventions are often not as powerful.
In emerging economies such as India, utility-scale solar and onshore wind power are proving significant access to capital. However, many clean energy applications, often of greatest importance to socio-economically and climate-vulnerable communities, can fall outside the scope of traditional finance.
This report aims to identify and suggest options to fill this gap in finance by exploring the potential of blended finance structures. By elucidating concepts around blended finance and providing insights to enhance its applicability, this report offers a roadmap for interventions in segments struggling to secure traditional finance. Masu.
This report delves into the architecture of blended finance solutions and shows how a bespoke framework can reduce financial risks associated with projects, products, target communities, markets and technologies. Particular emphasis is placed on the role of blended finance in expanding the solar PV mini-grid segment.
This report serves as a comprehensive guide for financial institutions looking to navigate blended finance structures for the energy transition. Development and commercial investors often approach opportunities with nuanced goals. Blended finance emerges as a mechanism to leverage the respective strengths of both these segments. Additionally, this document serves as a pathway for companies operating within the energy ecosystem, providing insights to increase preparedness and meet the specific standards required by financiers. Moreover, this could serve as a valuable resource for policymakers and advocate the adoption of more facilitative policies to facilitate the integration of blended finance into India's low-carbon energy transition opportunities. Finally, it could also serve as a blueprint for other emerging countries facing similar challenges to India to devise financing mechanisms for the energy transition.