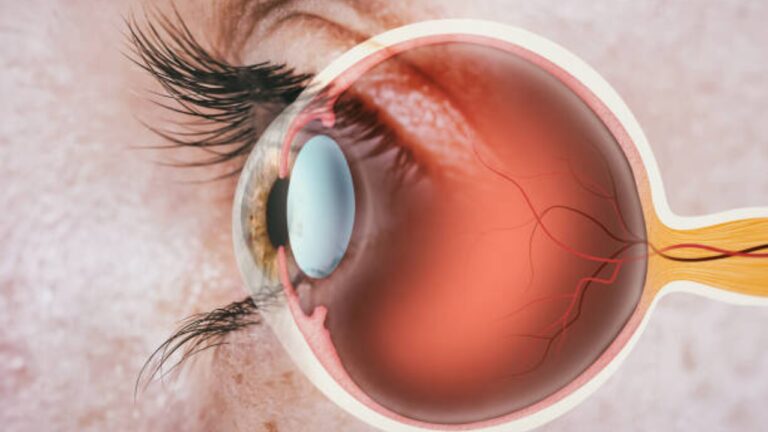
What is glaucoma?
Glaucoma refers to a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve, often as a result of increased pressure within the eye. This damage can lead to vision loss, which can lead to blindness if left untreated. Glaucoma is often asymptomatic in its early stages, earning it the nickname “the silent thief of vision.” Regular eye exams are very important for early detection and treatment.
How are diabetes and glaucoma related?
Diabetes primarily affects blood sugar levels and insulin function, but it can also have significant effects on eye health, including an increased risk of developing glaucoma. Diabetes can damage blood vessels throughout the body, including the eyes. These vascular changes can affect fluid circulation within the eye and lead to increased intraocular pressure (IOP), a known risk factor for glaucoma.
Both diabetes and glaucoma can damage the optic nerve. In diabetes, high blood sugar levels can cause diabetic retinopathy, a condition that can damage blood vessels in the retina and eventually affect the optic nerve. Similarly, in glaucoma, increased IOP can cause progressive damage to optic nerve fibers.
It's important to control diabetes
“If left uncontrolled, diabetes can affect every part of the eye, including the eyelids, cornea, crystalline lens, retina, and blood vessels of the eye, and it can also affect intraocular pressure,” says Endocrinology and Diabetes, Max Super Specialty Hospital, Vaishali. says consultant Dr. Aishwarya Krishnamurthy. he told IANS.
Expanding
“Diabetes is the leading cause of blindness in working-age people. Blood vessels in the retina can swell and leak fluid into the eye. If untreated, it can lead to vision loss and the retina moving from its normal position at the back of the eye. It can lead to serious problems such as retinal detachment, which can lead to detachment,” added Dr Surender Kumar, senior endocrinologist at Sir Ganga Ram Hospital.
Dr Rajeev Gupta, head of internal medicine at Delhi's CK Birla Hospital, told IANS that diabetes is associated with many other eye diseases that can impair vision, including diabetic retinopathy, cataracts, glaucoma, macular edema and dry eye. He said it also increases the risk. If left undiagnosed and untreated, it can even lead to blindness.
According to a recent study published in The Lancet, around 21 million people in India are visually impaired, of whom 2.4 million are visually impaired. This number is expected to increase further as diabetes, a significant risk factor for vision loss, is rapidly increasing in the country.
How can I prevent glaucoma?
Managing diabetes and glaucoma requires a multidisciplinary approach that includes regular medical care, lifestyle modifications, and adherence to a treatment plan.
People with diabetes need to monitor their blood sugar levels, manage their diabetes medications and insulin therapy, and address any complications promptly. Similarly, people with glaucoma should have regular eye exams to monitor intraocular pressure and optic nerve health, and receive appropriate treatment if necessary.
Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, weight management, and smoking cessation can help manage both diabetes and glaucoma. Lifestyle modifications that promote overall health and well-being can also reduce the risk of diabetes-related eye complications and slow the progression of glaucoma.
For people with diabetes or glaucoma, regular eye exams are essential to monitor changes in vision, assess optic nerve health, and detect early signs of diabetic retinopathy or glaucoma progression. Timely intervention and treatment can help preserve vision and prevent further damage to the eye.
(With inputs from IANS)